This article has been reviewed by Sumeet Sinha, MBA (Emory University Goizueta Business School). Should you have any inquiries, please do not hesitate to contact at sumeet@finlightened.com.
Before we get into stock options trading, let’s see what a stock option is. So, what is an option? An option is a contract that you can purchase. It’s a ‘derivative’ that derives its value from underlying securities such as ETFs and stocks (read about ETFs vs stock picking). A Stock Option gives you the right to buy or sell stock at an agreed price on or before a particular date.
Types of Stock Options
What is a Call Option?
With the call option, the holder gets the right (but not the obligation) to purchase shares at an agreed-upon price on or before the expiration date.
What is a Put Option?
With the put option, the holder gets the right (but not the obligation) to sell the shares at an agreed-upon price on or before the expiration date.
- Read more about Call options
- Read more about Put options
To sum it up, both types of stock options can be used to bet on price movements in opposite directions. But, there are multiple combinations of buying & selling call options and put options that can be leveraged to maximize chances of gains and limit investors’ risks. Options trading is the act of transacting stock options to make financial gains and limit risk exposure at the same time.
What Are Stock Options?
Stock options are contracts that give investors the right (but not obligation) to buy or sell a stock at a certain price, before a certain date. Simply put, it’s a method of trading stocks on leverage.
For example, when you buy a call option, you buy the contract that will allow you to buy 100 shares of a stock at a fixed price (called the strike price). But, this contract is not valid indefinitely, it comes with an expiration date. The expiration date and the strike price play a crucial role in determining the price (premium) of the contract.
Similarly, when you buy a put option, you buy the contract that will allow you to sell 100 shares of a stock at a fixed price (called the strike price). Put options also come with an expiration date.
Basic Stock Options Trading Terminology
Premium:
The amount paid for purchasing a call or put option contract.
Strike Price:
The share price at which the call option contract allows you to buy the shares. In case of put options, the strike price is the share price at which you can sell your shares.
Expiration:
The last day on which the call or put option can be exercised. It is the end of the validity of the contract.
Exercise:
The act of using the call option to actually buy the 100 shares at the given strike price. Similarly, it is the act of using the put option to actually sell 100 shares at the given strike price.
Intrinsic Value:
The price difference between the share price and the strike price of the option.
- For the call option, when the share price is higher than the strike value, intrinsic value = share price – strike price.
- For the put option, when the share price is lower than the strike price, intrinsic value = strike price – share price.
Delta:
Delta is the relative price movement in the price of the ‘option’ compared to the movement in stock price. For example, when the stock price moves up by $10, and the ‘premium’ rises by $7, delta = 70%.
Stock Options vs Stock
There are two main differences between stocks and stock options.
- You can buy individual shares like 1,2,3 shares or even fractional shares. But, when buying call or put options, you buy contracts on a lot of 100 shares typically.
- When you buy a stock, it does not have any expiration date. However, a stock option (call or put), it comes with an expiration date.
How do Stock Options Work?
If you believe a stock price will go up, you can buy call options to gain from the upside, by investing a fraction of the cost of the stock (100 shares per contract). Call options are a way to leverage your ‘long’ bets.
If you believe the stock price will go down, you can buy a put option to gain from the downside, by investing a fraction of the cost of the stock (100 shares per contract). Put options, like call options, are a way to leverage your ‘short’ bets. However, unlike call options where the potential gain is unlimited, put options get capped at the value of the strike price (x 100).
In The Money vs Out of Money Call Options
When the share price (e.g. $325) is above the strike price (e.g. $300) of the call option contract, the call is considered in the money. That’s because the option is theoretically worth some money (intrinsic value), in this case, $325 – $300 = 25 per share. On the flip side, when the share price (e.g. $295) is below the strike price (e.g. $300) of the call option contract, the option is considered out of money. That’s because theoretically, the call option is worthless (no intrinsic value).
In The Money vs Out of Money Put Options
When the share price (e.g. $325) is below the strike price (e.g. $350) of the put option contract, the put is considered in the money. When the share price is above the strike price of the put option contract, the put option is considered out of money.
How are Stock Options Taxed?
There are two ways taxes are considered when trading options – one for individual stock options, and one for options on index funds (such as the S&P500 index fund). Gains in trading individual stock options are treated as ordinary income and taxed using the ‘short-term tax rate’. Gains in trading options on index funds are treated differently – 60% is taxed at a ‘long-term tax rate’ and the remaining 40% is taxed at a ‘short-term tax rate’.
We are NOT tax advisors, please consult a tax advisor for the most updated tax laws in your region
Where to Learn Stock Options Trading?
Let’s discuss where to learn options trading and how long it takes for an average person to learn options trading. In the industry, the average amount of time required for a newbie investor to reach the junior trader level of options trading is 6 months to two years. Everyone has their own speed, but one must make sure to fully understand the risks of options trading before even putting a cent into options trading.
You can learn options trading from multiple resources, but it is important to learn the concepts well. There are many courses on the internet from which you can learn- both paid and free.
On our website, we have attempted to cover all aspects of options in an easy-to-understand manner. You can also gather a reasonable amount of information to step into options trading from Youtube. YouTube is home to multiple experts who post informative videos regarding options trading with live examples.
Why have an Options Trading Strategy?
Generally, for most investors, you can’t make money with stocks when the market goes down or trade sideways. That is where options come in. Options allow you to make money in any market condition – whether the market goes up, down, or sideways. You can make money in any situation in options by leveraging different strategies.
Options trading offers many advantages if you learn the tricks of the trade. One of the main benefits of options trading is that it lets you commit less capital while buying options than while purchasing stocks directly.
How to Start Trading Stock Options?
To start trading, you must meet the requirements. You must be approved for options trading through your broker. The broker will ask you to fill out a questionnaire. The questions will be about your investing experience, financial status, and knowledge of trading options. Some brokers will NOT allow you access to options trading if they believe you are not knowledgeable enough about the risks of investing. We believe this is a very good guardrail in place as it prevents you from making an uninformed decision and losing your money.
Read Related
Why is Trading Stock Options Risky?

Options trading carries asymmetric risk. While the gains are accelerated, the losses can be accelerated too. In case of a worthless options expiration, the investor (option buyer) loses all the premium paid for it, losing the entire capital!
There is a limited time frame for the investment to play out in your favor. The options traders need to take advantage of relative price movement within the contract timeframe, i.e. before the expiration date. This requires speculating – deciding when to buy, sell, exercise, or let the option expire.
Options trading is considered risky mostly because of the leveraged capital loss. Some strategies are considered risky because of the complexity involved with them. Due to time differences across borders, international trading options have additional risks.
Bestseller Personal Finance Books
To avoid letting beginner investors make unintentional mistakes with options, brokerages categorize the investors into different levels. Read about Levels in Options Trading.
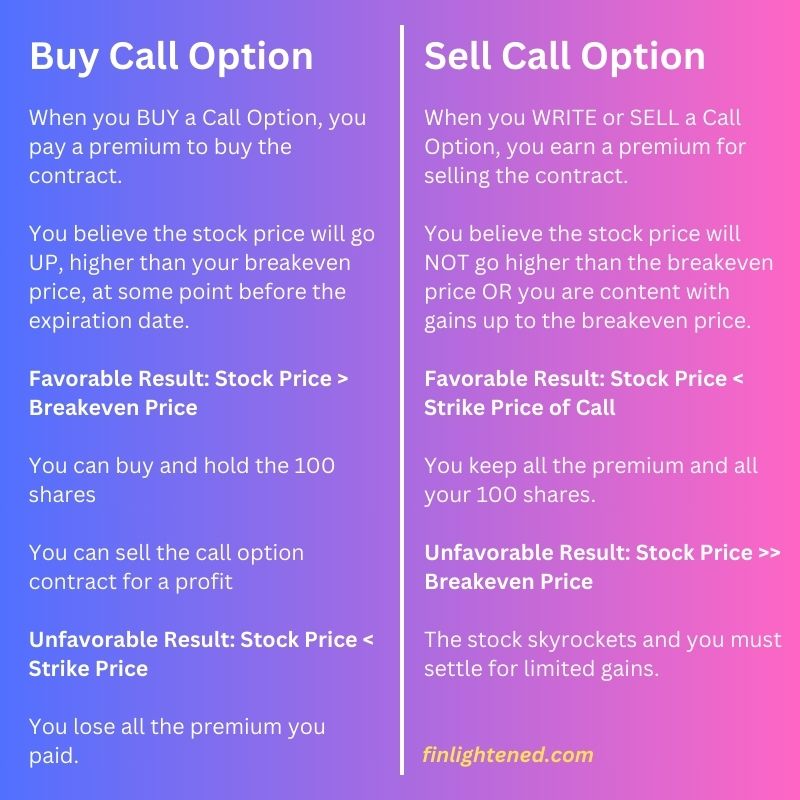
When to Buy or Sell Call Options?
The chart below gives a general idea of when you might want to either buy or sell a call option.
Buy Call Option
When you BUY a Call Option, you pay a premium to buy the contract.
You believe the stock price will go UP, higher than your breakeven price, at some point before the expiration date.
Favorable Result: Stock Price > Breakeven Price
- You can buy and hold the 100 shares
- You can sell the call option contract for a profit
Unfavorable Result: Stock Price < Strike Price
You lose all the premium you paid.
Sell Call Option
When you WRITE or SELL a Call Option, you earn a premium for selling the contract.
You believe the stock price will NOT go higher than the breakeven price OR you are content with gains up to the breakeven price.
Favorable Result: Stock Price < Strike Price of Call
You keep all the premium and all your 100 shares.
Unfavorable Result: Stock Price >> Breakeven Price
The stock skyrockets and you must settle for limited gains.
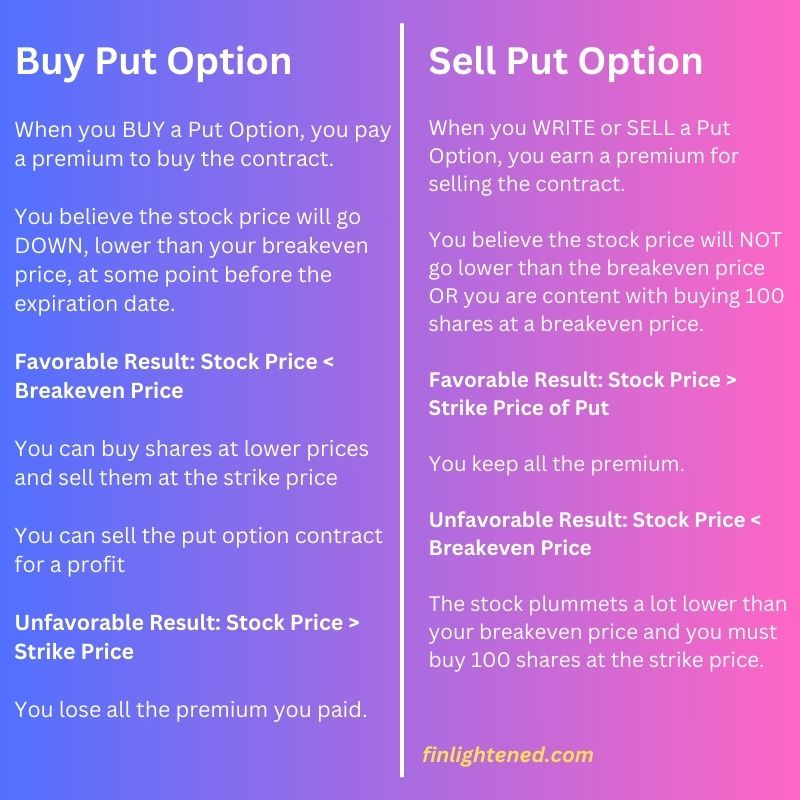
When to Buy or Sell Put Options?
The chart below gives a general idea of when you might want to either buy or sell a put option.
Buy Put Option
When you BUY a Put Option, you pay a premium to buy the contract.
You believe the stock price will go DOWN, lower than your breakeven price, at some point before the expiration date.
Favorable Result: Stock Price < Breakeven Price
You can buy shares at lower prices and sell them at the strike price
You can sell the put option contract for a profit
Unfavorable Result: Stock Price > Strike Price
You lose all the premium you paid.
Sell Put Option
When you WRITE or SELL a Put Option, you earn a premium for selling the contract.
You believe the stock price will NOT go lower than the breakeven price OR you are content with buying 100 shares at a breakeven price.
Favorable Result: Stock Price > Strike Price of Put
You keep all the premium.
Unfavorable Result: Stock Price < Breakeven Price
The stock plummets a lot lower than your breakeven price and you must buy 100 shares at the strike price.
Where can I Buy and Sell Stock Options?
Most stockbrokers allow qualified investors, based on the questionnaire as mentioned above, to trade options. Even on newer platforms such as Robinhood and Webull, investors can start with stock options for low or no fees. The legacy brokerages might have better analytics and features, with quick trade execution times, but beginners and intermediates will find the newer brokers a good fit for their needs.
Check out the Levels in Options Trading to understand why a broker may let you perform certain options trades depending on your experience and risk tolerance levels.

Read more
Popular Topics: Stocks, ETFs, Mutual Funds, Bitcoins, Alternative Investing, Dividends, Stock Options, Credit Cards
Posts by Category: Cash Flow | Credit Cards | Debt Management | General | Invest | Mini Blogs | Insurance & Risk Mgmt | Stock Market Today | Stock Options Trading | Technology
Useful Tools
Student Loan Payoff Calculator | Mortgage Payoff Calculator | CAGR Calculator | Reverse CAGR Calculator | NPV Calculator | IRR Calculator | SIP Calculator | Future Value of Annuity Calculator
Home | Blog
Our Financial Calculator Apps
Page Contents