This article has been reviewed by Sumeet Sinha, MBA (Emory University Goizueta Business School). Should you have any inquiries, please do not hesitate to contact at sumeet@finlightened.com.
Before we dive deep into the FOMC Meetings and Fed Funds Rate (check the current Fed Funds Rate), let’s understand what FOMC is, what Federal Reserve is, and how FOMC relates to the Federal Reserve.
Unemployment Rate, CPI Inflation, GDP Growth Rate, Fed Funds Rate Today
| Unemployment Rate 1 | 3.8% [March 2024] |
| CPI Change % YOY 2a | 3.5% [March 2024] |
| PCE Change YOY 2b | 2.7% [March 2024] |
| GDP Growth Rate % YOY 3 | +1.6% [Q1 2024 (Adv est.)] |
| Fed Funds Rate 4 | 5.33% [March 2024] |
1 U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Unemployment Rate [UNRATE], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/UNRATE
2a U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, CPI for All Urban Consumers (CPI-U), not seasonally adjusted. https://data.bls.gov/timeseries/CUUR0000SA0&output_view=pct_12mths
2b The U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Index. https://www.bea.gov/
3 U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Gross Domestic Product. https://www.bea.gov/data/gdp/gross-domestic-product
4 Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), Federal Funds Effective Rate [FEDFUNDS], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/FEDFUNDS
Mortgage Rates Today
See below for the live mortgage interest rates today in the United States.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Countdown To FOMC Meeting [Statement Release Time]
Quick View: 2024 FOMC Meetings and Rate Hikes
| December 17 -18 | TBA |
| November 6 – 7 | TBA |
| September 17 – 18 | TBA |
| July 30 – 31 | TBA |
| June 11 – 12 | TBA |
| April 30 – May 1 | TBA |
| March 19 -20 | no rate change |
| Jan 30 – Jan 31 | no rate change |
Quick View: 2023 FOMC Meetings and Rate Hikes
| December 12 -13 | no rate hike |
| October 31 – Nov 1 | no rate hike |
| September 19 – 20 | no rate hike |
| July 25 -26 | +25 bps |
| June 13 -14 | no rate hike |
| May 2 – 3 | +25 bps |
| March 21 -22 | +25 bps |
| Jan 31- Feb 1 | +25 bps |
What is the Federal Reserve? Is It Part Of The Government?
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the “Fed,” is the central banking system of the United States. It was established in 1913 through the Federal Reserve Act. The Federal Reserve’s main objective is to maintain a stable and secure financial system while promoting the economic well-being of the country (United States).
The Federal Reserve operates independently of the government but is subject to oversight from Congress. It consists of several key components: the Board of Governors, regional Federal Reserve Banks, and the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).
The Board of Governors, located in Washington, D.C., is the central decision-making body of the Federal Reserve. It consists of seven members who are appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate. The Chair of the Board of Governors is considered the public face of the Federal Reserve and plays a crucial role in shaping monetary policy.
There are twelve regional Federal Reserve Banks located across major cities in the United States. These banks serve as the operating arms of the Federal Reserve system, providing banking services to depository institutions and implementing monetary policy within their respective regions.
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is responsible for setting the nation’s monetary policy. It comprises the seven members of the Board of Governors and a rotating group of five regional Federal Reserve Bank presidents. The FOMC meets regularly to assess economic conditions and make decisions regarding interest rates and other monetary policy measures.
The Federal Reserve plays a critical role in managing the nation’s money supply, regulating banks, and fostering financial stability. It aims to promote full employment, stabilize prices, and maintain moderate long-term interest rates to support sustainable economic growth.
Where are the 12 Regional Federal Reserve Banks located in the US?
The 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks are located in the following cities:
- Boston, MA
- New York, NY
- Philadelphia, PA
- Cleveland, OH
- Richmond, VA
- Atlanta, GA
- Chicago, IL
- St. Louis, MO
- Minneapolis, MN
- Kansas City, MO
- Dallas, TX
- San Francisco, CA
What is FOMC or Federal Open Market Committee?
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) holds a crucial role as the decision-making body responsible for formulating monetary policy within the Federal Reserve System. It consists of 12 members, including the seven members of the Board of Governors and five of the 12 Reserve Bank presidents.
Bestseller Personal Finance Books
The Chair of the Board of Governors also serves as the Chair of the FOMC, while the President of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York assumes the role of Vice Chairman.
The remaining four voting positions are filled by the presidents of other Reserve Banks on a rotating basis.
All Reserve Bank presidents, even those without voting rights, actively participate in FOMC meetings, contribute to discussions, and provide insights on economic conditions and policy options. The current list of FOMC members can be accessed for reference.
How Many FOMC Meetings Are Conducted In A Year?
The FOMC convenes eight times annually, with meetings typically spaced approximately six weeks apart. However, additional unscheduled meetings may be called when necessary to assess economic and financial developments. Following each regular meeting, the FOMC issues a policy statement summarizing the Committee’s economic outlook and the policy decision made during that gathering.
Moreover, the Chair conducts a press briefing after each FOMC meeting, offering in-depth insights into the Committee’s policy choices and providing context to support understanding.
When Is The Next FOMC Meeting?
The list of scheduled FOMC Meetings for 2024 is mentioned below:
- Jan 30 – 31
- March 19 – 20
- April 30 – May 1
- June 11 – 12
- July 30 – 31
- September 17 – 18
- November 6 – 7
- December 17 – 18
The list of scheduled FOMC Meetings for 2023 is mentioned below:
- Jan 31- Feb 1
- March 21 -22
- May 2 – 3
- June 13 -14
- July 25 -26
- September 19 – 20
- October 31 – Nov 1
- December 12 -13

The list of FOMC Meetings that happened in 2022 is mentioned below:
- Jan 25 – 26
- March 15 – 16
- May 3 – 4
- June 14 -15
- July 26 – 27
- Sept 20 – 21
- November 1 – 2
- December 13 – 14
What is the Fed Funds Rate?
The Fed Funds Rate, Fed Rate, or the Federal Funds Rate is the interest rate for overnight intra-bank borrowing and lending transactions.
In other words, the Fed Funds Rate is the interest rate at which one bank borrows money from another bank for a short period of time to maintain its money reserve requirements (as mandated by the Federal Reserve).
It is sometimes also called “overnight rate”.
What does it mean – “Fed increased interest rate by 25 basis points or 0.25% at the FOMC meeting”?
News headlines such as “Fed increased interest rate by 25 points at the FOMC meeting” or “Fed decreased interest rate by 25 points at FOMC meeting” refer to an increase or decrease in the Fed Funds Rate.
25 basis points or 25 bps simply means 0.25%. So, an increase of 25 basis points on the current Fed Funds rate of 4% (say) will bring the new Fed Funds rate up to 4.25%.
How Has The Fed Funds Rate Changed Historically?
To get a full picture of historical changes in the Fed Funds Rate, we can refer to the St. Louis Fed website.
The chart below is from the website and shows the increases and decreases in the Fed Funds rate from 1955 to 2023.
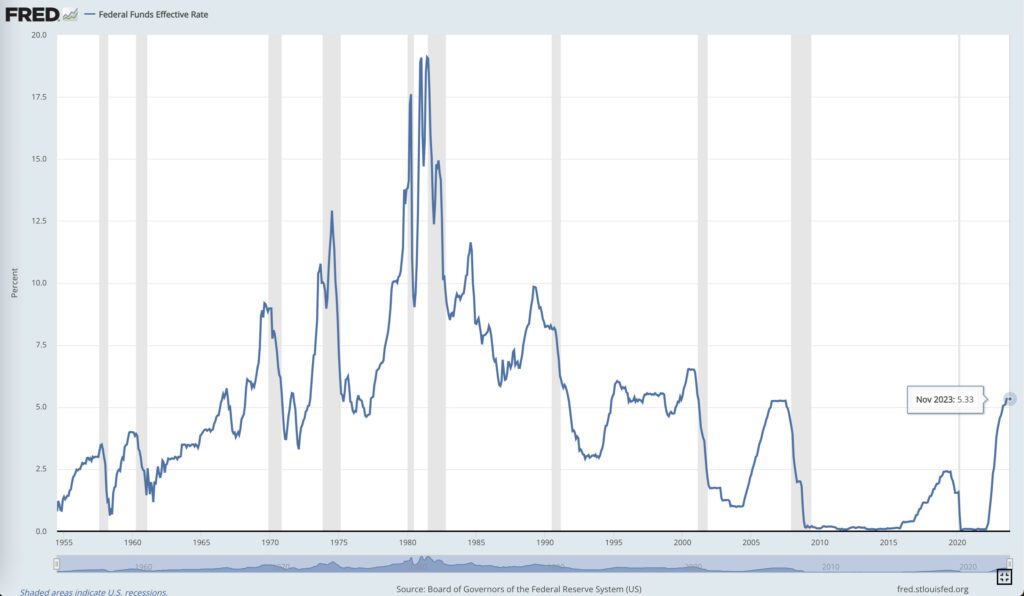
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), Federal Funds Effective Rate [FEDFUNDS], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/FEDFUNDS, December 14, 2023.
How many times has the interest rate increased in the last two years at FOMC meetings?
See below for the Fed Funds Rate hikes in the years 2022 and 2023. In the year 2022 alone, the Fed Funds rate was increased by 425 bps or 4.25 percentage points.
2023 FOMC Meetings and Rate Hikes
| December 12 -13 | no rate hike |
| October 31 – Nov 1 | no rate hike |
| September 19 – 20 | no rate hike |
| July 25 -26 | +25 bps |
| June 13 -14 | no rate hike |
| May 2 – 3 | +25 bps |
| March 21 -22 | +25 bps |
| Jan 31- Feb 1 | +25 bps |
2022 FOMC Meetings and Rate Hikes
| December 13 – 14 | +50 bps |
| November 1 – 2 | +75 bps |
| Sept 20 – 21 | +75 bps |
| July 26 – 27 | +75 bps |
| June 14 -15 | +75 bps |
| May 3 – 4 | +50 bps |
| March 15 – 16 | +25 bps |
| Jan 25 – 26 | 0 bps |
How Does The Fed Funds Rate Impact Me?
We have learned that the Fed Funds Rate is the interest rate for banks to borrow and lend money among themselves, so why should the common man be worried about it at all?
The answer is that the Fed Funds Rate has a direct downstream impact on the common people. When banks get loans at a higher interest rate – they pass on the increased rate to the consumers who may want to borrow some money from a bank for buying a house, buying a car, starting a business, investing in real estate, investing in the stock market, or any other purpose.
Higher interest rates make it more difficult for common people to take out loans.
How Does The Fed Funds Rate Impact The Economy?
A high Fed Funds Rate makes it more difficult for people and businesses and investors to borrow money. This in turn reduces the demand for things in general – for example, the mortgage rate goes up – fewer people can afford the monthly payments – so fewer people are looking to buy a new house.
See the chart below to understand the impact of the Fed Funds Rate on mortgage rates.
Fed Funds Rate vs. 30-Year Fixed Rate Mortgage
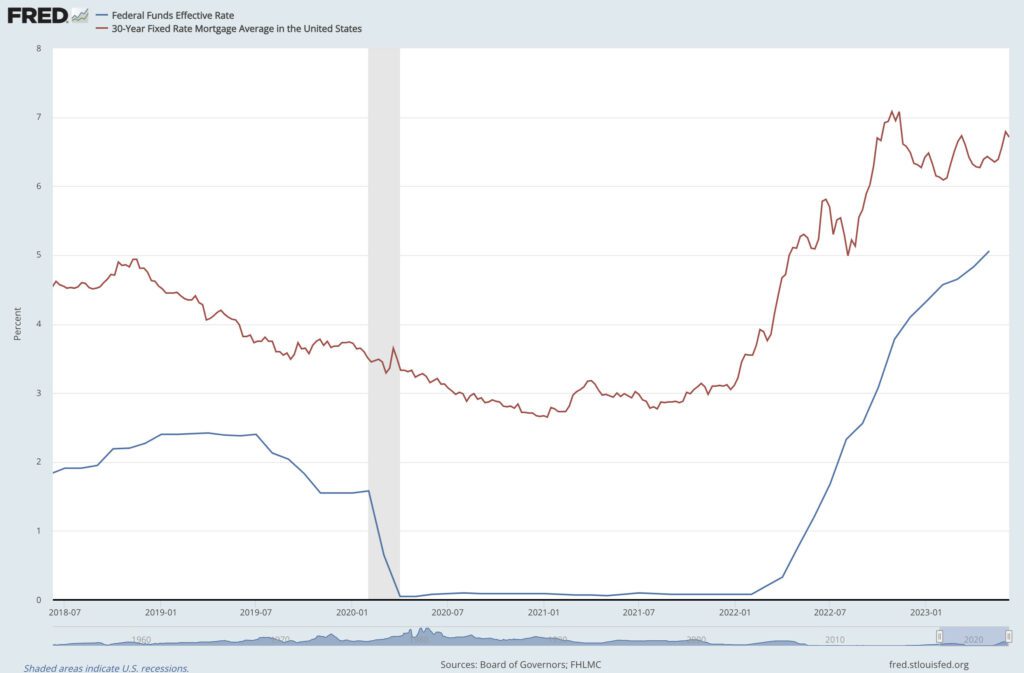
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), Federal Funds Effective Rate [FEDFUNDS], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/FEDFUNDS, June 13, 2023.
Source: Freddie Mac, 30-Year Fixed Rate Mortgage Average in the United States [MORTGAGE30US], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/MORTGAGE30US, June 13, 2023.
By increasing the Fed Funds Rate, the demand in the market can be controlled. As demand comes down, the price of things comes down over time.
So, a primary concern during the FOMC meetings is to keep a check on ‘inflation‘, and by controlling the Fed Funds rate, the demand hence prices hence inflation can be controlled.


Read more
Popular Topics: Stocks, ETFs, Mutual Funds, Bitcoins, Alternative Investing, Dividends, Stock Options, Credit Cards
Posts by Category: Cash Flow | Credit Cards | Debt Management | General | Invest | Mini Blogs | Insurance & Risk Mgmt | Stock Market Today | Stock Options Trading | Technology
Useful Tools
Student Loan Payoff Calculator | Mortgage Payoff Calculator | CAGR Calculator | Reverse CAGR Calculator | NPV Calculator | IRR Calculator | SIP Calculator | Future Value of Annuity Calculator
Home | Blog
Our Financial Calculator Apps
Page Contents















